The Organization
A public Spanish university hospital operating in care, research, and education, featuring 53 specialties. The hospital is a national and international reference in various areas of high scientific and technological development.
The Challenge
The challenge was to improve the hospital’s emergency service to optimize patient flow, streamlining the triage, discharge, and transfer processes.
To achieve this, the main patient flows were identified. A general mapping of these patient routes through a Value Stream Analysis (VSA) was performed, along with data collection, to detect improvement opportunities. These opportunities were then prioritized based on the workflow impact and implementation level of difficulty.
The Approach
For each line of work, different actions to implement were considered:
Admissions and Triage
- Normalize the work and generate flexibility: two fixed triage stations and a third flexible station on demand to handle patient influx peaks;
- Eliminate non-value-added administrative tasks, such as non-priority calls and standardization of information recorded during the process;
- Optimize computer tools to achieve pull-based appointment assignments and rapid visualization of room occupancy;
- Physically define the admission queue zone to avoid blocking passage areas;
- Define the triage waiting room and standardize the patient call process, one by one, and always with a buffer of one patient to ensure flow and minimize waiting times.
Bed Management, Transfers, and Pre-Discharges
- Define an early discharge protocol to increase bed availability in the ward during the early hours of the day;
- Streamline and standardize the automated discharge process as well as bed assignment so that the time from ward discharge to emergency discharge is minimized;
- Optimize using the pre-discharge room to increase bed availability in the ward.
Room Management
- Assign patients to rooms based on their category: unstable, high comorbidity, waiting for admission, under 24-hour observation…
- Reduce the average room occupancy to 80%, adjusting each room’s capacity to patient demand.
Complaints Reduction
To reduce the number of both verbal and written complaints, the following actions were planned:
- Standardize the information on the health status given to relatives and communicate estimated waiting times;
- Allow open room visits limited to one person and for a set amount of time;
- Implement a lost items protocol.
Optimization of the Medical Assistant Circuit
- Make it easier to coordinate assistant nurse requests by centralizing them.
- Record all services to be performed in a ward so that available assistants know the pending tasks, allowing them to be autonomous and work without the need for assistance, and also know how many tasks are pending in each ward;
- Create a priority definition protocol adapted to the care load;
- Improve the coordination of patient transfers to the ward to avoid waiting times;
- Balance the beds in the emergency service and ward to facilitate “bed by bed” admission, reducing the time spent by assistants and cleaning staff.
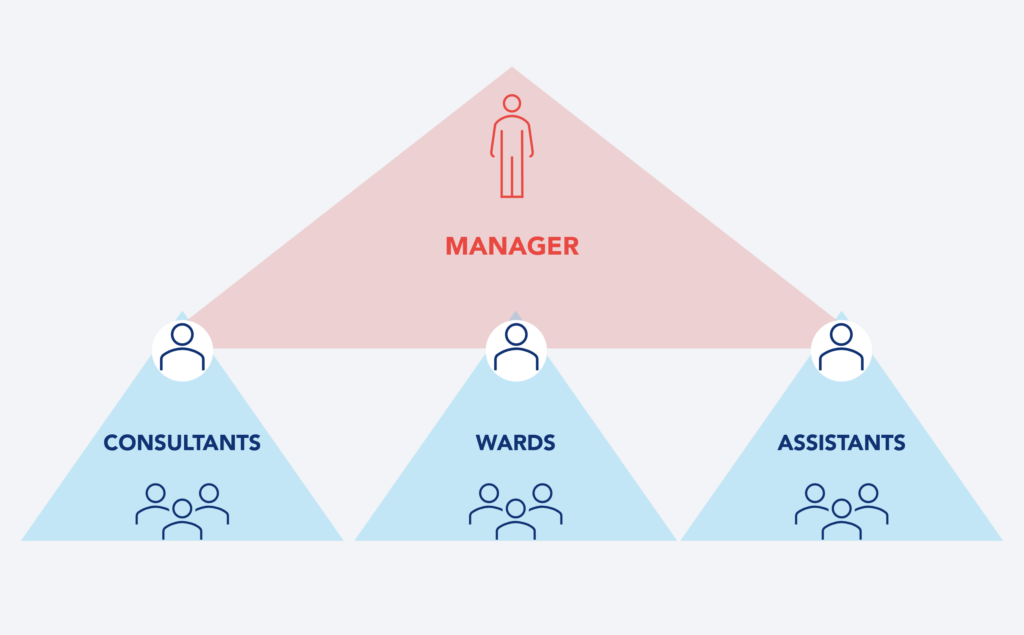
Team Management
To conduct team management dynamics and organize day-to-day work, review the emergency service indicators to detect deviations from set objectives, and plan continuous improvement actions, a Daily KAIZEN™ model at three levels was proposed:
- Leaders KAIZEN™: to review and streamline the Emergency Department overall state, as well as set the priorities for the day;
- Middle management: to distribute information from the leaders’ meeting to their respective teams;
- Wards: organization of daily operations within them.
Work Standardization within Rooms
- Track electronically each patient’s location;
- Reorganize work materials – mobile carts, material stations, pyxis system, etc. – so that they are located where needed, do not block passage areas, and are safe;
- Coordinate internal work by creating Doctor-Nurse-Assistant Nurse teams;
- Balance the load of each room through a management function that ensures correct patient distribution, avoiding imbalances.
Emergency Room Optimization
- Reduce the occupation of the emergency room by certain types of patients;
- Streamline the service request form process;
- Define the action sequence in case of an emergency notice to reduce waiting times;
- Organize work and define areas.
Layout Optimization
A spaghetti diagram analysis was conducted to reduce movements and flows for the main types of patients. With this information and based on data-driven motion optimization, layout changes were proposed, such as creating a waiting area for admissions.
Emergency Communication and Signage System
Using a loudspeaker for communication complicates the work of staff and the rest of the patients. To decrease its usage, replacing it with another form of communication was suggested.
The signaling system has also been improved to reduce patient confusion and avoid interruptions to staff. Other actions defined include color-coded instructions, admission station numbering, and increasing the size of the signs.
The Results
Once the bottlenecks and challenges were identified, as well as the impact of new strategies in each area and service, the cost-benefit of the proposed improvements was estimated.
The optimization of the discharge process would free up 60 beds per day. In admission and triage, a 32% increase in productivity and a 17.5% reduction in processing times are expected. As for complaints, they would decrease by 24%, thus increasing patients’ and relatives’ satisfaction. The management model for the assistant nurse team would improve productivity by 10%. Regarding the emergency room and the new room organization, the productivity of all involved staff would increase by 8%.
These benefits, which would also impact cost reduction, would come with an improvement in the employees’ satisfaction and motivation.
See more on Healthcare
Find out more about transformation in this sector
See more on Administration & Services
Find out more about improving this business area
