The success of a business depends more than ever on effective customer relationship management strategies. A proper CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system can be a differentiating factor for companies of all sizes and industries, enabling efficient management of customer interactions, increasing sales, improving service, optimizing the link between marketing and sales, and driving growth. However, given the numerous options, choosing the best CRM for every business can take time and effort.
This article will explore the essential steps to selecting the CRM best suited to each company’s needs, from understanding the organization’s specific needs to evaluating features, usability, security, cost, and support.
Understand the company’s needs
Understanding the organization’s specific needs is critical to selecting the best CRM. Understanding the company’s goals will help define the requirements and functionalities. On the other hand, it is essential also to consider the long-term strategy. If, for instance, the plan is to expand into new markets, a CRM with scalability capabilities and support for multiple teams may be critical.
Besides thoroughly understanding the company’s needs, each department and team may have specific CRM needs. Therefore, it is essential to survey the needs of different areas, such as sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support, to understand which features are most relevant for each department. Thus, finding a CRM that meets all the needs and promotes collaboration between the teams will be possible.
It is time to identify the essential requirements and list the indispensable features and functionalities based on evaluating the company’s goals and each department’s needs. Some common examples of CRM functionality are contact management, sales management, marketing automation, campaign and lead management, customer service, analytics and reporting, and task management.
By surveying the essential requirements, one has a solid basis for comparing the CRM options available and ensuring that the system chosen meets the company’s needs.
Evaluate the CRM options available
Several types of CRM are available, each with its characteristics and benefits. Exploring and understanding the different options is essential to identify which CRM best suits one’s needs. Some of the most common types include:
- On-premises CRM: The software is installed on the company’s servers and managed in-house, and this can offer more control and customization, but it requires its IT infrastructure and regular maintenance;
- In-cloud CRM: Also known as SaaS CRM (Software as a Service), this type of CRM is accessible via the Internet and hosted on the provider’s servers. It is more flexible regarding remote access, automatic updates, and scalability.
- Open-source CRM: Developed and maintained by the programmers’ community. It is highly customizable and provides a solid foundation to tailor to the company’s specific needs.
When deciding on these types of CRMs, it is necessary to consider the company’s characteristics, such as the size of the team, the security and accessibility requirements for the tool, and the available IT infrastructure.
Each CRM has a different set of features and functionality. During the research, it is crucial to identify which features are essential for the company and compare CRM systems in terms of these capabilities.
Usability and User Interface
An effective CRM should be intuitive and easy to use so that users can take full advantage of its features. When evaluating the user-friendliness of a CRM, one must consider the ease of navigation and customization. The interface should be intuitive, with an easy-to-understand menu structure. On the other hand, the CRM should allow you to customize the interface according to user preferences. Features such as the ability to customize layouts, fields, and reports can increase productivity and tailor the CRM to the company’s needs.
The user experience also plays a vital role in adopting and effectively using CRM. When evaluating the user experience, consider design and layout, and responsiveness. The CRM interface should have a clean and organized look and feel. On the other hand, it is essential to check whether the CRM has a responsive interface that adapts to different devices and screen sizes. This allows users to use the CRM most conveniently on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
A good CRM should provide training resources to ensure users can use all the system’s features effectively. Check if the provider offers adequate training through documentation, video tutorials, webinars, or in-person training.
Data security and privacy
Protecting company and customer data is critical. When evaluating a CRM, it is essential to check the security measures implemented by the supplier to protect the data stored in the system. One should consider the following aspects: encryption, access control, and data backup and recovery.
With the growing importance of data protection, it is also essential to ensure that the CRM complies with laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union.
Finally, the CRM supplier’s privacy policy is an important document. One should read the privacy policy to understand how the supplier collects, stores, uses, and protects customer data. Ensure the privacy policy is clear, transparent, and meets data protection standards. And one must remember that the exact location of the servers can be a factor in the decision process.
CRM integration and scalability
When choosing a CRM, it is critical to consider its ability to integrate with other systems used by the company. Efficient integration allows CRM to become part of the organization’s software ecosystem, improving productivity and facilitating information sharing. When evaluating CRM integration, one should consider the following points: integration with productivity tools, marketing automation systems, and customer support systems.
Another crucial factor when selecting a CRM is scalability. As the company grows, the CRM must be able to handle an increase in the number of users, volume of data, and complexity of operations. When evaluating the CRM’s scalability, the following points should be considered:
- Number of users: Check whether the CRM can accommodate an increasing number of users without compromising performance;
- Data volume: Make sure that the CRM can store and manage large volumes of data as the company grows. This includes contact information, sales history, customer interactions, and other relevant data;
- Flexibility and customization: Verify that the CRM can be customized and configured to meet the business’s specific requirements as it grows.
Reputation and support of the CRM supplier
Before choosing a CRM, it is important to research the supplier’s reputation. This can be accomplished by consulting market research on CRM providers, online research on ratings and comments from other users, and CRM-related online communities.
Having efficient and reliable support is essential when buying a CRM. It is necessary to consider the following aspects when evaluating the support offered by the supplier:
- Customer service: Check whether the provider offers different support channels, such as phone, live chat, or email support. Also, evaluate the response times and availability of support.
- Updates and bug fixes: Check how the CRM vendor works with software updates and bug fixing.
Cost and Return on Investment
When selecting the best CRM for the business, it is essential to consider the cost incurred and the expected return on investment (ROI).
When evaluating the costs of different CRM options, consider the following aspects:
- Subscription plan: Check the different price models, such as a lifelong license or monthly/yearly subscription. Also, consider whether there are additional costs for additional user licenses or an additional number of contacts.
- Maintenance and support: Some CRM options may include setup, maintenance, and support in the license cost, while others may charge a separate fee. Evaluate what is included and verify that the support offered reflects the needs.
- Upgrades and improvements: Consider whether CRM upgrades and improvements are included in the cost or whether there are additional costs for future upgrades.
When analyzing the CRM’s added value and expected return on investment, consider the following points:
- Functionalities and resources: Evaluate the functionalities offered by the CRM and how they meet the company’s needs. Consider whether the CRM offers additional resources, such as marketing automation, data analytics, or multi-channel support, that can bring significant benefits to the business;
- Increased productivity: Consider how CRM can improve the productivity of sales, marketing, and customer service teams. Evaluate whether CRM offers features that automate repetitive tasks and streamline processes.
- Improved customer service: See if CRM enables better tracking and management of customer interactions, which can lead to more personalized and effective customer service. Assess how this can impact customer satisfaction and, consequently, increase sales and loyalty.
Calculating the expected ROI can be complex, as it involves estimating the benefits and costs over time. Factors such as time savings, increased sales, reduced errors, and improved productivity must be considered.
When comparing payment options, consider each model’s cost, flexibility, and scalability.
Testing and demonstrations
Finally, before making a final decision, it is recommended to ask for demonstrations of the CRM from the suppliers under consideration.
Along with demonstrations, it is essential to conduct practical tests with actual company data and scenarios. This allows us to evaluate the CRM performance in an environment similar to the company’s. Consider the following steps during testing:
- Import real data: Import real company data into the CRM and observe how the system handles that data. Evaluate the ease of import, the quality of the data transferred, and the integrity of the records.
- Test use scenarios: Perform practical tests by running relevant use scenarios. This might include lead creation, sales opportunity management, tracking customer interactions, and more. Observe how the CRM facilitates these tasks and meets expectations.
- Usability Evaluation: During testing, evaluate the usability of the CRM. Check if the interface is intuitive, the features are easy to find, and the browsing is straightforward.
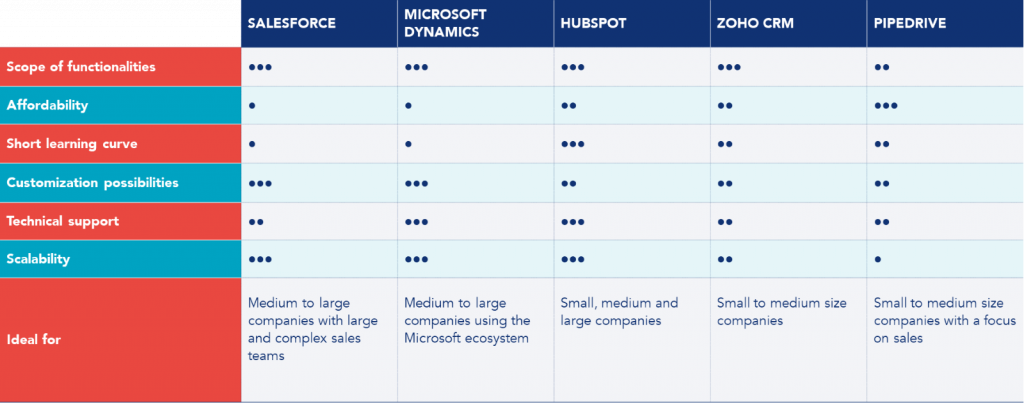
Main CRM on the market – best options for each case
There are many different CRM options available in the market. We will now explore the five most widely used and well-known CRMs: Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics, HubSpot, Pipedrive, and Zoho CRM. Each offers unique features and functionality to meet the changing needs of the different types of businesses.
Salesforce
Considered one of the CRM market leaders, Salesforce is known for its wide range of features and flexibility. It offers comprehensive sales management, marketing, customer service, and data analytics solutions.
Main advantages:
- Broad range of features: It offers a wide range of features and functionality for sales, marketing, and customer service management.
- Customization and scalability: It is highly customizable and scalable, allowing companies to adapt the platform to their needs.
- Ecosystem and integrations: It has a vast ecosystem of applications and integrations, allowing companies to connect to other tools and systems
Main disadvantages:
- Complexity and long learning curve: Due to its wide range of features, Salesforce CRM can be complex for inexperienced users, requiring time and training to master the platform entirely.
- High cost: It is more expensive than most other options available. Advanced plans and features can come at a significant cost, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
- Customer support: Although it offers customer support, some users report that support can be slow or that responses are not entirely satisfactory.
Microsoft Dynamics
Microsoft is a brand known for its global presence and reliability in various industries. Microsoft Dynamics is a comprehensive solution that fully integrates with other Microsoft products. It offers advanced sales, marketing, and customer service features, allowing teams to collaborate and share information efficiently. It is mainly used by companies already using Microsoft products.
Main advantages:
- Integration with the Microsoft ecosystem: One of the main advantages is its seamless integration with other Microsoft solutions, such as Microsoft 365, SharePoint, and Outlook. This makes it easy to synchronize data, collaborate between teams, and access important information in a single familiar environment.
- Customization and flexibility: Offers a high level of customization and flexibility to meet the specific needs of each business.
- Strong support and community: Microsoft has robust technical support and an active community of users and programmers. This means that a wide range of resources are available, such as documentation, discussion forums, and tutorials, that can help resolve issues and maximize the use of CRM.
Main disadvantages:
- Long learning curve: It can have a long learning curve. The interface and system structure can be complex for inexperienced users, requiring time and training to become thoroughly familiar with the platform.
- Dependency on other Microsoft products: While integration with other Microsoft products is an advantage, it can be a disadvantage for companies that do not use them. Dependence on the Microsoft ecosystem can restrict flexibility and choice of integrations with other tools or systems.
- Licensing and cost: Licensing Microsoft Dynamics CRM can be complex and may involve additional costs, especially for advanced features or custom needs. The total cost can be substantial for some organizations, especially small to mid-sized businesses.
HubSpot
It is a CRM and marketing platform designed to help businesses attract, engage, and convert leads into customers. Besides traditional CRM functionality, HubSpot offers a range of digital marketing features, such as marketing automation, content management, and performance analytics. With a customer-centric approach, HubSpot enables companies to create a personalized customer journey and deliver a consistent experience across all channels.
Main advantages:
- Free features: Offers a free version with essential CRM features, allowing small businesses or teams with limited budgets to access a CRM solution with no upfront costs. This can be a significant advantage for companies starting or wanting to experiment before investing in a paid solution.
- Wide range of Marketing resources: Allows a complete view of the customer lifecycle, from lead generation to closing a sale. The integration facilitates lead capture, lead nurturing, interaction tracking, and marketing automation, providing a more cohesive experience for sales and marketing teams.
- Intuitive and user-friendly interface: It has a friendly and intuitive interface, making it easy to navigate and use. This reduces the learning curve and accelerates team-wide adoption of the platform. In addition, it provides training and support resources to help users maximize usage.
Main disadvantages:
- Increasing costs with expansion: As the company grows and its CRM needs become more complex, upgrading to HubSpot’s paid plans may be necessary. This transition can significantly increase costs, especially if the company needs additional features like marketing automation or priority support.
Zoho CRM
The solution offers sales automation, marketing, customer service, and pipeline management features. Zoho CRM is known for its customizable interface, allowing companies to tailor the system to their specific needs. In addition, Zoho CRM offers integration with other Zoho applications, such as Zoho Books and Zoho Campaigns, providing a comprehensive solution for companies looking to centralize business processes on a single platform.
Main advantages:
- Full feature set: Offers a complete set of sales, marketing, and customer service management features. It includes sales automation, lead tracking, account management, marketing campaigns, customer support, and more. This scope of features allows companies to have a holistic view of operations and improve the efficiency of their teams.
- Customization and flexibility: It is highly customizable and flexible, allowing companies to adapt the platform to their needs. It allows custom fields, automated workflows, and custom mixed reports creation.
- Integration with other Zoho tools: It integrates seamlessly with other tools from the Zoho ecosystem, such as Zoho Desk, Zoho Campaigns, Zoho Books, and others. This integration makes it easy to synchronize data, collaborate across teams, and create automated workflows, providing a more integrated experience for sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
Main disadvantages:
- Complex interface for beginners: For first-time users, Zoho CRM’s interface may be complex and require more time to adapt. The navigation and structure of the system may not be as intuitive as other CRM solutions available on the market.
- Additional cost for advanced features: Although Zoho CRM offers a free version, some advanced features and specific functions may require upgrading to a paid plan. Getting priority support or advanced support features may require upgrading to a paid plan.
Pipedrive
It is a CRM designed for small and medium-sized business teams. With its focus on the sales pipeline and process automation, Pipedrive simplifies the management of leads, negotiations, and contacts. It offers an intuitive and easy-to-use interface that allows users to track sales progress in a structured way.
Main advantages:
- User-friendly and intuitive interface: The platform is designed for easy navigation and understanding, allowing users to familiarize themselves with the system quickly. This facilitates the adoption and use of CRM across the team.
- Efficient sales funnel management: Enables efficient management of the sales funnel. It allows one to easily view and track the sales process stages, from prospecting to closing the sale.
- Customization and automation: Offers customization and automation features that allow companies to adapt the CRM to their specific needs. It enables the creation of custom fields, the definition of automated workflows, and the setting of reminders and notifications to track customer interactions.
Main disadvantages:
- Limited scalability: While it is suitable for small to mid-sized businesses, it may have limitations when it comes to scalability. It does not offer the same range of features and functionality as other more robust CRM platforms.
- Limited marketing features: Pipedrive’s primary focus is sales management, which means that marketing features are relatively limited compared to other CRMs.
- Advanced customization requires technical expertise: While Pipedrive offers customization features, the advanced configuration may require technical expertise or the help of a developer.
Conclusion
Although the CRM market is vast, Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics, Pipedrive, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM are some of the most widely used and trusted CRMs. Each offers a unique combination of resources, features, and pricing, addressing the diverse needs of businesses of different sizes. When considering implementing a CRM system, it is essential to carefully evaluate the company’s needs and choose the solution that best aligns with business goals and strategies.
In short, for companies to select the best CRM for their specific needs, they should:
- Perform a complete analysis of the company’s needs, considering specific targets, goals, and requirements of each department;
- Research and evaluate different CRM options, considering features, functionality, compatibility, and integration with other software used by the company;
- Evaluate usability, considering ease of use and user experience;
- Verify the security measures implemented by the CRM, ensuring compliance with the laws in force;
- Research the support offered by the CRM vendor and verify the satisfaction of other customers;
- Consider the cost and return on investment by comparing the costs of CRM options and assessing the expected value.
- Perform practical tests and ask for demonstrations to understand the operation and adaptability of the CRM to the company’s processes.
By following these guidelines, a company will be on track to select the best CRM, optimize processes and achieve more efficient results.
CRM is a strategic and long-term decision, so it is essential to invest time and effort in researching and evaluating the options available to ensure that the CRM best suited to the organization’s needs and goals is chosen.
See more on Sales & Marketing
Find out more about improving this business area
