The commercial department is the heartbeat of an organisation. It triggers the rest of the organisation’s operations, adapting to do so in the most efficient and productive way known so far. The commercial activity presupposes the knowledge of the customer and also of the challenges, the knowledge of the product or service and its characteristics, as well as the ability to adjust the offer throughout the relationship with the customer, with sole focus on their satisfaction. Controlling these variables and team management, is still a challenge for some commercial teams, which can obstruct the path towards sales excellence.
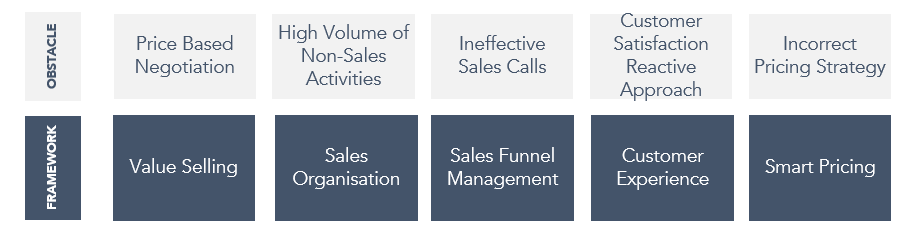
1. Price Based Negotiation
In most business to business (B2B) interactions, sales teams choose a price-based negotiation model, as the discussion is based on the product / service value to the customer, it requires a more substantial and deeper level of knowledge. By choosing this approach, the benefits for the customer will not be maximised, as solutions adapted to their real needs are not offered, but instead “off-the-shelf” options. This inflexibility in the debate about the product on offer leads to the loss of valuable insights for product development, which could lead to a market share gain or new niche.
The trend towards price-based negotiation can also arise from the difficulty of making a challenging argument. This is a skill that cannot be left to the mercy of experience and should be worked on from the very beginning by the team.
2. High Volume of Non-Sales Activities
The second paradigm to consider is the time that teams dedicate to everything that is considered non- sales activities. In fact, about 64% of a salesperson’s time is dedicated to these tasks. Among these are administrative tasks, internal meetings, management tasks, and others, meaning only 34% of time is dedicated to sales related activities. Therefore, it should not come as a surprise that results fall short ideal.
Reversing this trend requires special focus on reorganising the sales department. The starting point for this restructuring is identifying which tasks add real value for sales and isolate those that, although necessary, do not. After this step, these tasks can be simplified and reallocated to concentrate them on one section of the team, increasing productivity, and focusing the sales teams on their main goal-selling.
3. Ineffective Sales Calls
85% of customers consider most meetings with salespeople as not adding value. Thus, to close a sale, several more interactions with the customer are necessary to overcome this lack of content. Extending the commercial process Lead Time increases the risk of losing the sale and may be related to the low overall conversion rate for B2B interactions, which is around 25%.
To tackle this issue, it is necessary to properly plan and prepare the meeting with the customer. This preparation should focus on product / service information relevant to the customer concerned, reviewing the customer’s purchase history and behaviour and adaptation of the approach based on the customer’s position in the sales funnel. It is crucial that teams have the existing leads, their status and purchase history and information regarding challenges / needs at their disposal. With frequent analysis of this information, it becomes possible to analyse funnel penetration and conversion indicators, leading to solid action plans to solve deviations from the goal.
4. Customer Satisfaction Reactive Approach
Another crucial aspect for market follow-up is gathering of customer satisfaction data. Most organisations choose to measure their customers’ satisfaction through satisfaction surveys or through their complaints. However, this approach has several not so positive aspects.
Assessing customer satisfaction through their complaints is a high risk, reactive process, as the organisation is only acting when the customer has already reached a high state of concern. In the age of online information, an unsatisfied customer’s opinion can be shared rapidly, causing a wave of bad publicity for the organisation. The ideal follow-up of the customer and adjustment to the customer’s needs and requirements can, in most cases, avoid these complaints and lead to a prosperous business relationship.
As far as surveys are concerned, these are an excellent tool for collecting standardised information from a large sample. However, the advantage regarding information processing simplicity and access to a large volume of respondents is offset by the loss in information quality. A closed and standardised survey leaves little room for sharing specific experiences and insights from each customer.
Real involvement of customers in the product / service design process can be done through interviews that effectively capture their vision and experience. These should be conducted in a customised way for sectors and activities, using a script of open-ended questions with flexibility for creativity in the feedback provided.
5. Incorrect Pricing Strategy
There are countless pricing strategies that an organisation can choose to pursue, which makes it difficult to define the one that is best suited in each context. The most common strategy is cost-plus pricing, where a margin is added after calculating the costs of the product or service to be offered. Nevertheless, the use of such a simplistic strategy without in-depth study of the market characteristics may lead to high losses of potential profits, damaging the positioning of the product/service among its competitors.
The commercial area is crucial to any organisation. In the information age it is essential that commercial teams abandon total dependence on the experience of each team member and implement focused and structured tools for dealing with the market in which they operate. Each obstacle to excellence must be worked on to achieve breakthrough results and a strong competitive advantage. It is time to demystify the concept of a “good salesperson” and make it accessible to the teams of any organisation.
Structured Approach to Activities and Sales Teams
#marketing and sales
See more on Marketing & Sales
Find out more about improving this business area
